ESP32-C3-Zero Pro is a development board based on the ESP32C3 microcontroller using RISCV32 architecture.
This board features a maximum CPU frequency of 160 MHz and 4MB flash memory.
About ESP32-C3-Zero Pro
ESP32-C3-Zero Pro is an upgraded version of the ESP32-C3-Zero, featuring a better ceramic antenna and an IPEX antenna mount for improved wireless performance. It is based on the Espressif ESP32-C3 Wi-Fi/Bluetooth dual-mode chip, with a 32-bit RISC-V single-core processor running at up to 160 MHz. It comes with 400 KB SRAM, 384 KB ROM, and 4 MB of onboard flash memory.
This board supports 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi (802.11 b/g/n) and Bluetooth 5 (LE), making it ideal for low-power IoT applications and wireless wearable devices. 📶
Compared to the ESP32-C3-Zero, the Zero Pro offers enhanced signal strength due to its dual-antenna design, making it more reliable for applications requiring strong wireless connectivity. It retains the same ultra-compact footprint (22.52 × 18 mm) while adding more connectivity options.
For user convenience, it includes both a RESET button and a BOOT button to facilitate development and debugging. 🚀
The board provides 11 digital I/O pins configurable as PWM outputs and 4 analog I/O pins for ADC inputs. It supports multiple serial interfaces, including 1× I2C, 1× SPI, and 2× UART, ensuring compatibility with a wide range of peripherals. ⚙️
Where to Buy ESP32-C3-Zero Pro
Prices are subject to change. We earn from qualifying purchases as an Amazon Associate.
Technical Specifications
Complete technical specification details for ESP32-C3-Zero Pro
Connectivity
Microcontroller
✨ Features & Pins
- • Improved wireless performance: Better ceramic antenna + IPEX antenna mount
- • Ultra-small size: 22.52 × 18 mm
- • Ultra-low power consumption: deep sleep current approximately 43 μA
- • Onboard blue LED connected to GPIO8
Quick Setup
Copy-paste configs for ESP32-C3-Zero Pro - auto‑generated from this board's exact hardware specs.
In Arduino IDE 2 select Esp32c3 Dev from the esp32 by Espressif package. In PlatformIO use board = esp32-c3-devkitm-1. ESP32C3 · 160 MHz · 4MB · QIO · RISC-V.
In Arduino IDE 2, open Boards Manager, search "esp32" by Espressif and install it. Then go to Tools → Board and select "Esp32c3 Dev" for the ESP32-C3-Zero Pro.
[env:esp32-c3-zero-pro]
platform = espressif32
board = esp32-c3-devkitm-1
framework = arduino
; Exact hardware config for ESP32-C3-Zero Pro
board_build.mcu = esp32c3
board_build.f_cpu = 160000000L
board_build.flash_size = 4MB
board_build.flash_mode = qio
board_upload.flash_size = 4MBThe board value is a close generic match - check PlatformIO board registry for an exact fit.
esp32:
board: esp32-c3-devkitm-1
framework:
type: arduino # or "esp-idf"
# ESP32-C3-Zero Pro - 160 MHz ESP32C3
# Flash: 4MB | USB: N/APaste into your device's .yaml. See ESPHome ESP32 docs for full options.
esptool.py \
--chip esp32c3 \
--baud 921600 \
write_flash \
--flash_mode qio \
--flash_size 4MB \
0x0 bootloader.bin \
0x8000 partitions.bin \
0xe000 boot_app0.bin \
0x10000 firmware.binInstall: pip install esptool - replace firmware.bin with your binary - bootloader at 0x0
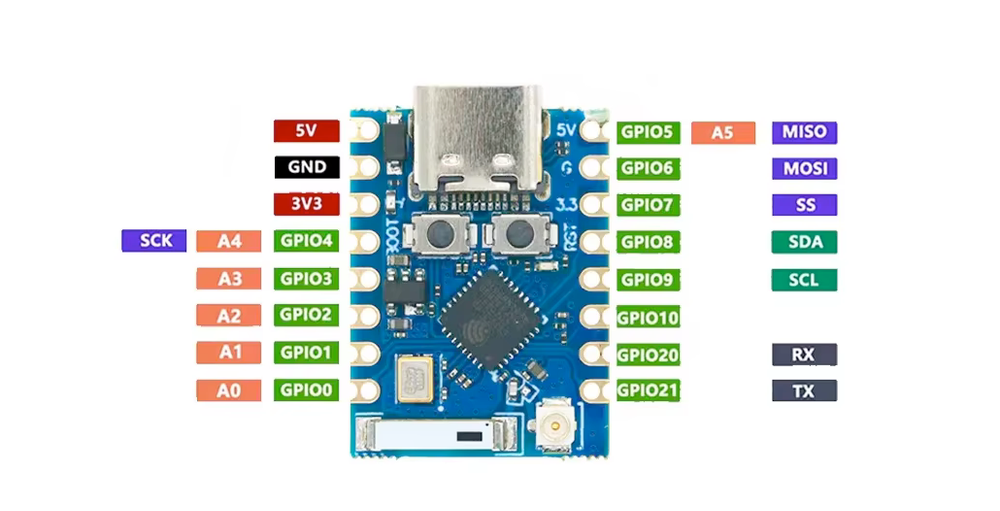
ESP32-C3-Zero Pro Pinout Diagram
Complete pin reference for ESP32-C3-Zero Pro
The ESP32-C3-Zero Pro pinout is designed for versatility in a compact form factor. Key power pins include 5V, 3.3V, and GND, ensuring stable power delivery for various peripherals.
The board provides multiple communication interfaces:
- UART: TX, RX
- I2C: SDA, SCL
- SPI: SCK, MISO, MOSI, SS
For analog input, it offers ADC pins suitable for reading sensor data or voltage levels.
Safe Pins to Use
These pins are safe for general GPIO usage without boot or system conflicts
Why Are These Pins Safe?
Pins to Avoid or Use with Caution
Reserved for critical functions. Misuse may cause boot failures, programming issues, or system conflicts.
Boot behavior & flash voltage
Low-level debugging interface
USB Serial/JTAG communication
Memory & PSRAM connections
Debugging & firmware uploads
| PIN | Label | Why Avoid | Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| IO2 | GPIO2 | Must be held high during boot (if low on reset, normal flash boot may fail) | 🛠️ Strapping |
| IO4 | MTMS | Used during boot; JTAG TMS for debugging; acts as Quad-SPI flash IO (hold data line) in internal-flash variants | 🔗 JTAG |
| IO5 | MTDI | Used during boot; JTAG TDI for debugging; acts as Quad-SPI flash IO (write-protect data line) in internal-flash variants | 🔗 JTAG |
| IO6 | MTCK | Used during boot; JTAG TCK for debugging; provides flash clock in internal-flash variants | 🔗 JTAG |
| IO7 | MTDO | Used during boot; JTAG TDO for debugging; acts as Quad-SPI flash IO (data line) in internal-flash variants | 🔗 JTAG |
| IO8 | GPIO8 | Must be held high during reset (if low, UART flashing/boot may not work) | 🛠️ Strapping |
| IO9 | GPIO9 | Controls boot mode on reset (HIGH for normal flash boot, LOW enters serial download mode) | 🛠️ Strapping |
| IO20 | U0RXD | Used as UART0 receive (console/bootloader); repurposing may disable serial programming and debug logs | 📡 UART |
| IO21 | U0TXD | Used as UART0 transmit (console/bootloader); repurposing may disable serial console output and printing | 📡 UART |
Useful Links
Datasheets and resources for ESP32-C3-Zero Pro
ESP32-C3-Zero Pro Custom Pin Mapping
Pin configuration and GPIO mapping for ESP32-C3-Zero Pro
| Pin | Function | ESP Pin | I/O Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 5V | 5V | POWER INPUT | 5V power input for the board |
| 2 | GND | GND | POWER GROUND | Ground connection |
| 3 | 3V3 | 3.3V | POWER OUTPUT | 3.3V power output |
| 4 | IO0 | GPIO0 | BIDIRECTIONAL | GPIO, ADC, PWM |
| 5 | IO1 | GPIO1 | BIDIRECTIONAL | GPIO, ADC, PWM |
| 6 | IO2 | GPIO2 | BIDIRECTIONAL | GPIO, ADC, PWM |
| 7 | IO3 | GPIO3 | BIDIRECTIONAL | GPIO, ADC, PWM |
| 8 | IO4 | GPIO4 | BIDIRECTIONAL | GPIO, ADC, SPI SCK, PWM |
| 9 | IO5 | GPIO5 | BIDIRECTIONAL | GPIO, ADC, SPI MISO, PWM |
| 10 | IO6 | GPIO6 | BIDIRECTIONAL | GPIO, SPI MOSI, PWM |
| 11 | IO7 | GPIO7 | BIDIRECTIONAL | GPIO, SPI SS, PWM |
| 12 | IO8 | GPIO8 | BIDIRECTIONAL | GPIO, I2C Data line, PWM |
| 13 | IO9 | GPIO9 | BIDIRECTIONAL | GPIO, I2C Clock line, PWM |
| 14 | IO10 | GPIO10 | BIDIRECTIONAL | GPIO |
| 15 | IO20 | TX | BIDIRECTIONAL | GPIO, UART Transmit |
| 16 | IO21 | TX | BIDIRECTIONAL | GPIO, UART Transmit |
Default Tools & Configuration
Build and upload settings for ESP32-C3-Zero Pro
| Setting | Value |
|---|---|
| Bootloader tool | esptool_py |
| Uploader tool | esptool_py |
| Network uploader tool | esp_ota |
| Bootloader address | 0x0 |
| Flash mode | qio |
| Boot mode | qio |
| Maximum upload size | 1280 KB (1310720 bytes) |
| Maximum data size | 320 KB (327680 bytes) |
The ESP32-C3-Zero Pro uses esptool_py for uploads , esp_ota for OTA updates, and esptool_py bootloader at 0x0.
Flash mode: qio | Boot mode: qio
Max sketch size: 1280 KB | Max data size: 320 KB
Similar Boards
Other development boards with ESP32C3 microcontroller
TTGO T-OI PLUS RISC-V ESP32-C3
TTGO T-OI PLUS RISC-V ESP32-C3 development board is based on esp32c3 microcontroller and uses riscv32...

WiFiduinoV2
WiFiduinoV2 development board is based on esp32c3 microcontroller and uses riscv32 architecture.
Adafruit QT Py ESP32-C3
Adafruit QT Py ESP32-C3 development board is based on esp32c3 microcontroller and uses riscv32 architecture.