ESP32 A02YYUW Waterproof Ultrasonic Distance Sensor
The A02YYUW is a waterproof ultrasonic distance sensor ideal for outdoor and industrial applications. With a measuring range of up to 4.5 meters and a durable build, it is perfect for detecting objects in harsh conditions. It operates using a UART interface and is compatible with microcontrollers like Arduino and ESP32.
⬇️ Jump to Code Examples
🔗 Quick Links
🛒 A02YYUW Price
ℹ️ About A02YYUW Waterproof Ultrasonic Distance Sensor
The A02YYUW is a waterproof ultrasonic sensor designed for precise distance measurement in harsh environments. With an IP67-rated enclosure, it is dustproof and waterproof, making it ideal for outdoor and industrial applications.
⚡ Key Features #
- Wide Measurement Range – Detects distances from 3 cm to 450 cm.
- IP67 Waterproof & Dustproof – Built for moist, outdoor, and industrial environments.
- Reliable UART Communication – Provides stable distance readings via a UART interface.
- Versatile Applications – Used in liquid level detection, obstacle avoidance, and proximity sensing.
The A02YYUW is a great choice for rugged IoT applications, ensuring reliable performance in challenging conditions. 🚀
⚙️ A02YYUW Sensor Technical Specifications
Below you can see the A02YYUW Waterproof Ultrasonic Distance Sensor Technical Specifications. The sensor is compatible with the ESP32, operating within a voltage range suitable for microcontrollers. For precise details about its features, specifications, and usage, refer to the sensor’s datasheet.
- Protocol: UART
- Measurement Range: 3 cm to 450 cm
- Resolution: 1 mm
- Accuracy: ±1 cm
- Operating Voltage: 3.3V to 5V DC
- Average Current: <8 mA
- Response Time: 100 ms
- Interface: UART
- Operating Temperature: -15°C to 60°C
- Waterproof Grade: IP67
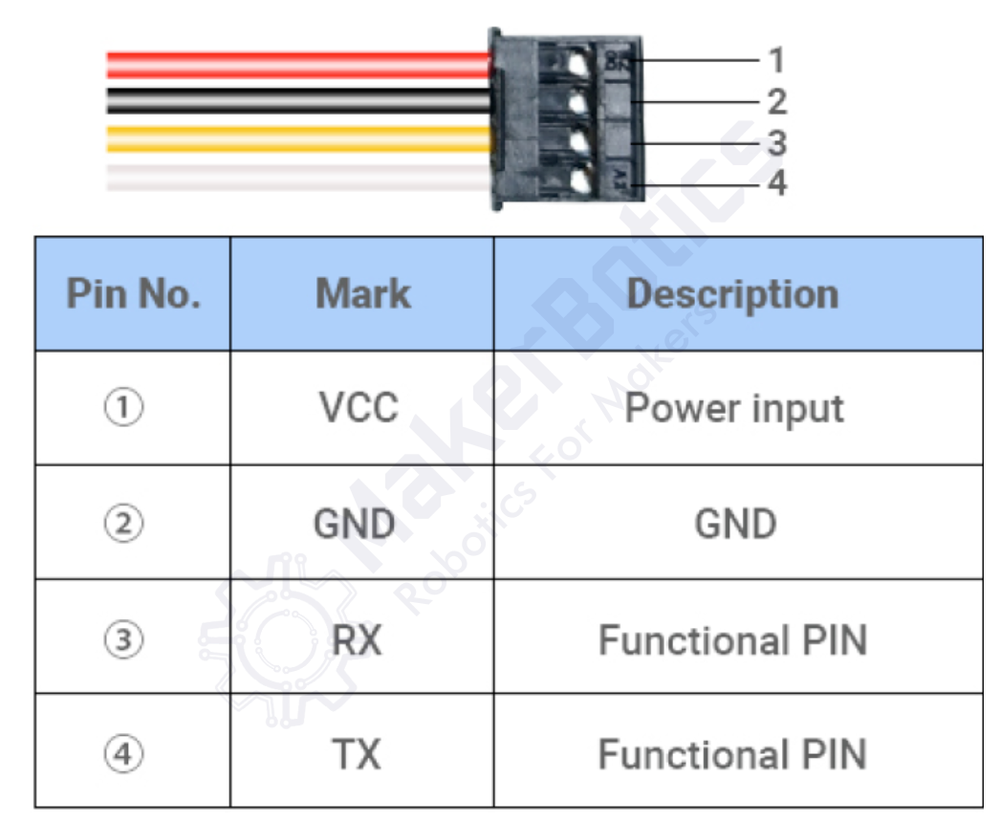
🔌 A02YYUW Sensor Pinout
Below you can see the pinout for the A02YYUW Waterproof Ultrasonic Distance Sensor. The VCC pin is used to supply power to the sensor, and it typically requires 3.3V or 5V (refer to the datasheet for specific voltage requirements). The GND pin is the ground connection and must be connected to the ground of your ESP32!
The A02YYUW pinout is as follows:
- VCC: Connect to a 3.3V to 5V power supply.
- GND: Ground connection.
- RX: UART receive pin for communication.
- TX: UART transmit pin for communication.
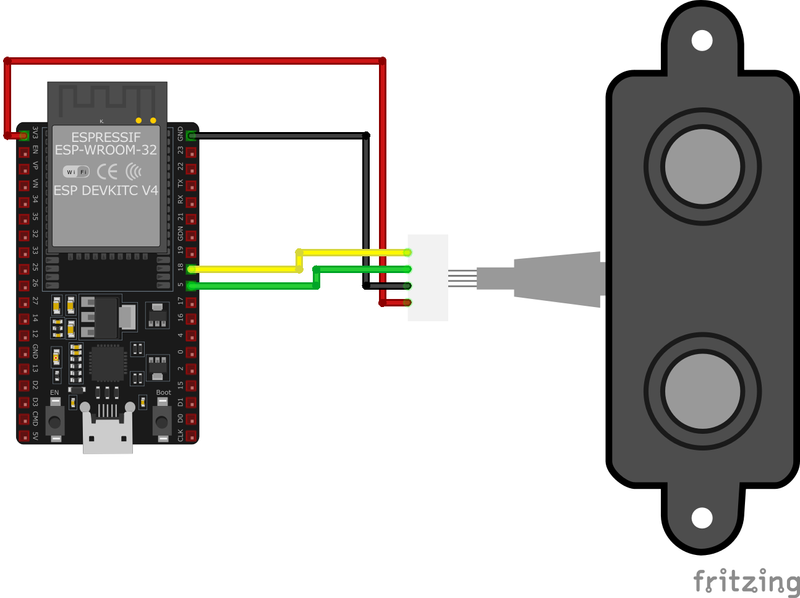
🧵 A02YYUW Wiring with ESP32
Below you can see the wiring for the A02YYUW Waterproof Ultrasonic Distance Sensor with the ESP32. Connect the VCC pin of the sensor to the 3.3V pin on the ESP32 or external power supply for power and the GND pin of the sensor to the GND pin of the ESP32. Depending on the communication protocol of the sensor (e.g., I2C, SPI, UART, or analog), connect the appropriate data and clock or signal pins to compatible GPIO pins on the ESP32, as shown below in the wiring diagram.
VCC to a 3.3V or 5V power source, GND to ground, TX to the microcontroller's RX pin, and RX to the microcontroller's TX pin. Ensure that the UART communication parameters are set to 9600 baud rate, 8 data bits, 1 stop bit, and no parity.🛠️ A02YYUW Waterproof Ultrasonic Distance Sensor Troubleshooting
This guide outlines a systematic approach to troubleshoot and resolve common problems with the . Start by confirming that the hardware connections are correct, as wiring mistakes are the most frequent cause of issues. If you are sure the connections are correct, follow the below steps to debug common issues.
🔄 Sensor Returns Constant or Erroneous Readings
Issue: The A02YYUW ultrasonic sensor provides constant or incorrect distance measurements, regardless of the actual distance to the target.
Possible causes include incorrect wiring, insufficient power supply, or improper sensor configuration.
Solution: Ensure that the sensor is connected to a stable 5V power source, as it requires 5V for proper operation. Verify that the sensor's TX (transmit) and RX (receive) lines are correctly connected to the corresponding RX and TX pins on the microcontroller, respectively. Confirm that the baud rate for serial communication is set to 9600 bps, as required by the sensor.
📉 Inconsistent or Fluctuating Distance Measurements
Issue: The sensor outputs distance readings that vary significantly, even when the target distance remains constant.
Possible causes include environmental factors such as temperature variations, soft or angled target surfaces, or electrical noise.
Solution: Position the sensor perpendicular to a hard, flat target surface to ensure accurate reflections. Be aware that temperature changes can affect the speed of sound; consider implementing temperature compensation if precise measurements are required. Implement averaging of multiple readings in your code to mitigate occasional erroneous data.
🚫 Sensor Not Detected or Unresponsive
Issue: The microcontroller fails to detect the A02YYUW sensor, or the sensor does not respond to trigger signals.
Possible causes include incorrect pin assignments in the code, lack of proper initialization, or defective sensor module.
Solution: Double-check the pin assignments in your code to ensure they match the physical connections. Confirm that the sensor is properly initialized in the setup section of your code. If the issue persists, test the sensor with a known working setup or replace it to rule out hardware failure.
🌍 Interference from Environmental Factors
Issue: External factors cause the sensor to produce unreliable readings.
Possible causes include high ambient noise levels, temperature variations, or obstacles in the sensor's field of view.
Solution: Operate the sensor in a controlled environment to minimize acoustic and electrical noise. Be aware that temperature changes can affect the speed of sound; consider implementing temperature compensation if precise measurements are required. Ensure that there are no unintended obstacles within the sensor's detection range that could cause false readings.
💻 Code Examples
Below you can find code examples of A02YYUW Waterproof Ultrasonic Distance Sensor with ESP32 in several frameworks:
If you encounter issues while using the A02YYUW Waterproof Ultrasonic Distance Sensor, check the Common Issues Troubleshooting Guide.

ESP32 A02YYUW Arduino IDE Code Example
Fill in your main Arduino IDE sketch file with the following code to use the A02YYUW Waterproof Ultrasonic Distance Sensor:
#include <Arduino.h>
// Define ESP32 hardware serial port for the A02YYUW sensor
#define A02YYUW_TX 18 // ESP32 TX connected to Sensor RX
#define A02YYUW_RX 5 // ESP32 RX connected to Sensor TX
// Initialize hardware serial for A02YYUW
HardwareSerial mySerial(2);
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200); // Initialize Serial Monitor
mySerial.begin(9600, SERIAL_8N1, A02YYUW_RX, A02YYUW_TX); // Initialize UART2
Serial.println("A02YYUW Distance Sensor Example");
}
void loop() {
if (mySerial.available() >= 4) {
uint8_t data[4];
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
data[i] = mySerial.read();
}
if (data[0] == 0xFF) { // Check packet start byte
int sum = (data[0] + data[1] + data[2]) & 0xFF;
if (sum == data[3]) { // Validate checksum
int distance = (data[1] << 8) + data[2]; // Calculate distance
if (distance > 30) { // Ensure valid reading
Serial.print("Distance: ");
Serial.print(distance / 10.0);
Serial.println(" cm");
} else {
Serial.println("Below the lower limit");
}
} else {
Serial.println("Checksum error");
}
}
}
delay(100);
}
This Arduino sketch interfaces with the A02YYUW ultrasonic distance sensor using ESP32's hardware serial (UART2) for stable communication.
Hardware Serial on ESP32 #
ESP32 has multiple hardware UART ports, eliminating the need for SoftwareSerial. This sketch uses UART2 (Serial2):
- TX (GPIO18) → Sensor RX
- RX (GPIO5) → Sensor TX
- Baud rate: 9600
Code Breakdown #
- Initialize UART2 with
mySerial.begin(9600, SERIAL_8N1, A02YYUW_RX, A02YYUW_TX); - Read sensor data (4-byte packets).
- Validate checksum for data integrity.
- Convert distance to cm and print it to the Serial Monitor.
- Error handling for checksum failures and out-of-range readings.
This setup ensures reliable distance measurement without using SoftwareSerial. 🚀
Connect your ESP32 to your computer via a USB cable, Ensure the correct Board and Port are selected under Tools, Click the "Upload" button in the Arduino IDE to compile and upload the code to your ESP32.

ESP32 A02YYUW ESP-IDF Code ExampleExample in Espressif IoT Framework (ESP-IDF)
If you're using ESP-IDF to work with the A02YYUW Waterproof Ultrasonic Distance Sensor, here's how you can set it up and read data from the sensor. Fill in this code in the main ESP-IDF file:
#include <stdio.h>
#include "driver/uart.h"
#include "esp_log.h"
#include "freertos/FreeRTOS.h"
#include "freertos/task.h"
#define RXD_PIN 16
#define TXD_PIN 17
#define UART_NUM UART_NUM_1
#define UART_BUFFER_SIZE (1024 * 2)
#define UART_TIMEOUT_MS 20
static const char *TAG = "UART_SENSOR";
void init_uart(void) {
// Configure UART parameters
const uart_config_t uart_config = {
.baud_rate = 9600,
.data_bits = UART_DATA_8_BITS,
.parity = UART_PARITY_DISABLE,
.stop_bits = UART_STOP_BITS_1,
.flow_ctrl = UART_HW_FLOWCTRL_DISABLE
};
// Apply UART configuration
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(uart_param_config(UART_NUM, &uart_config));
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(uart_set_pin(UART_NUM, TXD_PIN, RXD_PIN, UART_PIN_NO_CHANGE, UART_PIN_NO_CHANGE));
// Install UART driver with RX buffer and a small TX buffer
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(uart_driver_install(UART_NUM, UART_BUFFER_SIZE, 512, 0, NULL, 0));
// Set UART mode explicitly
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(uart_set_mode(UART_NUM, UART_MODE_UART));
}
void uart_task(void *pvParameters) {
uint8_t data[4];
while (1) {
// Read 4 bytes from UART
int len = uart_read_bytes(UART_NUM, data, 4, pdMS_TO_TICKS(UART_TIMEOUT_MS));
if (len == 4 && data[0] == 0xFF) {
// Calculate checksum
int sum = (data[0] + data[1] + data[2]) & 0xFF;
if (sum == data[3]) {
// Convert distance to centimeters
int distance = (data[1] << 8) | data[2];
if (distance > 30) {
ESP_LOGI(TAG, "Distance: %.2f cm", distance / 10.0);
} else {
ESP_LOGW(TAG, "Below the lower limit");
}
} else {
ESP_LOGE(TAG, "Checksum error (Received: 0x%02X, Expected: 0x%02X)", data[3], sum);
}
} else if (len > 0) {
ESP_LOGW(TAG, "Invalid data received");
}
vTaskDelay(pdMS_TO_TICKS(100));
}
}
void app_main(void) {
init_uart();
xTaskCreate(uart_task, "UART Task", 4096, NULL, 5, NULL);
}
This ESP-IDF code interfaces with the A02YYUW ultrasonic distance sensor using UART1 on the ESP32.
UART Configuration #
- TX (GPIO17) → Sensor RX, RX (GPIO16) → Sensor TX
- Baud rate: 9600, 8N1 format
- RX buffer: 2048 bytes
Code Breakdown #
- Initialize UART with
init_uart(), setting up UART parameters and driver. - Read Sensor Data in
uart_task(), processing 4-byte packets. - Validate Data by checking the header (0xFF) and checksum.
- Convert Distance from mm to cm and print it to the Serial Monitor.
A 100 ms delay ensures stable readings. 🚀
Update the I2C pins (I2C_MASTER_SDA_IO and I2C_MASTER_SCL_IO) to match your ESP32 hardware setup, Use idf.py build to compile the project, Use idf.py flash to upload the code to your ESP32.

ESP32 A02YYUW ESPHome Code Example
Fill in this configuration in your ESPHome YAML configuration file (example.yml) to integrate the A02YYUW Waterproof Ultrasonic Distance Sensor
uart:
tx_pin: GPIO5
rx_pin: GPIO18
baud_rate: 9600
sensor:
- platform: a02yyuw
name: "A02YYUW Distance"
update_interval: 100ms
timeout: 2sThe ESPHome configuration uses the uart platform to interface with the A02YYUW sensor. The tx_pin and rx_pin specify the GPIO pins used for UART communication. The baud_rate is set to 9600 to match the sensor's communication protocol. The sensor component configures the A02YYUW as the distance sensor, with a user-friendly name 'A02YYUW Distance.' The update_interval specifies that measurements are taken every 100 ms, and the timeout ensures reliable communication by preventing prolonged wait times for data.
Upload this code to your ESP32 using the ESPHome dashboard or the esphome run command.

ESP32 A02YYUW PlatformIO Code Example
For PlatformIO, make sure to configure the platformio.ini file with the appropriate environment and libraries, and then proceed with the code.
Configure platformio.ini
First, your platformio.ini should look like below. You might need to include some libraries as shown. Make sure to change the board to your ESP32:
[env:esp32dev]
platform = espressif32
board = esp32dev
framework = arduino
monitor_speed = 115200ESP32 A02YYUW PlatformIO Example Code
Write this code in your PlatformIO project under the src/main.cpp file to use the A02YYUW Waterproof Ultrasonic Distance Sensor:
#include <SoftwareSerial.h>
SoftwareSerial mySerial(5, 18); // RX, TX
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
mySerial.begin(9600);
Serial.println("A02YYUW Distance Sensor Example");
}
void loop() {
if (mySerial.available() >= 4) {
uint8_t data[4];
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
data[i] = mySerial.read();
}
if (data[0] == 0xFF) {
int sum = (data[0] + data[1] + data[2]) & 0xFF;
if (sum == data[3]) {
int distance = (data[1] << 8) | data[2];
if (distance > 30) {
Serial.print("Distance: ");
Serial.print(distance / 10.0);
Serial.println(" cm");
} else {
Serial.println("Below the lower limit");
}
} else {
Serial.println("Checksum error");
}
}
}
delay(100);
}The PlatformIO code communicates with the A02YYUW sensor via UART using the SoftwareSerial library. The RX and TX pins are defined on pins 5 and 18, respectively, and configured to operate at a 9600 baud rate. The code reads 4 bytes of data from the sensor, validates the header and checksum, and calculates the distance in millimeters. The distance is converted to centimeters and printed to the Serial Monitor every 100 ms.
Upload the code to your ESP32 using the PlatformIO "Upload" button in your IDE or the pio run --target upload command.

ESP32 A02YYUW MicroPython Code Example
Fill in this script in your MicroPython main.py file (main.py) to integrate the A02YYUW Waterproof Ultrasonic Distance Sensor with your ESP32.
from machine import UART
from time import sleep
# Configure UART
uart = UART(2, baudrate=9600, tx=5, rx=18)
def read_distance():
if uart.any() >= 4:
data = uart.read(4)
if data[0] == 0xFF:
checksum = (data[0] + data[1] + data[2]) & 0xFF
if checksum == data[3]:
distance = (data[1] << 8) | data[2]
if distance > 30:
return distance / 10.0
else:
return "Below the lower limit"
else:
return "Checksum error"
return None
print("A02YYUW Distance Sensor Example")
while True:
result = read_distance()
if result:
print(f"Distance: {result} cm")
sleep(0.1)This MicroPython script uses UART to communicate with the A02YYUW sensor. The UART is configured on TX pin GPIO17 and RX pin GPIO16 at a baud rate of 9600. The read_distance() function reads 4 bytes of data from the UART buffer, validates the header and checksum, and calculates the distance in millimeters. The result is converted to centimeters and returned. The main loop continuously calls this function every 100 ms to print the distance to the console. If the sensor detects an issue, such as a checksum error or a distance below the minimum threshold, appropriate messages are displayed.
Upload this code to your ESP32 using a MicroPython-compatible IDE, such as Thonny, uPyCraft, or tools like ampy.
Conclusion
We went through technical specifications of A02YYUW Waterproof Ultrasonic Distance Sensor, its pinout, connection with ESP32 and A02YYUW Waterproof Ultrasonic Distance Sensor code examples with Arduino IDE, ESP-IDF, ESPHome and PlatformIO.