ESP32 KY-032 Infrared Obstacle Avoidance Sensor Module
The KY-032 is an infrared obstacle avoidance sensor module that detects objects by emitting and receiving infrared light. It provides a digital output signal upon detecting an obstacle, making it suitable for applications like robotic navigation and object detection.
⬇️ Jump to Code Examples
🔗 Quick Links
🛒 KY-032 Price
ℹ️ About KY-032 Infrared Obstacle Avoidance Sensor Module
The KY-032 Infrared Obstacle Avoidance Sensor Module is designed to detect obstacles using infrared light. It emits infrared light, which, when reflected by an obstacle, is detected by a photodiode. The module outputs a digital signal indicating the presence or absence of an obstacle. This sensor is commonly used in robotics for obstacle detection and avoidance.⚙️ KY-032 Sensor Technical Specifications
Below you can see the KY-032 Infrared Obstacle Avoidance Sensor Module Technical Specifications. The sensor is compatible with the ESP32, operating within a voltage range suitable for microcontrollers. For precise details about its features, specifications, and usage, refer to the sensor’s datasheet.
- Protocol: Digital
- Operating Voltage: 3.3V to 5V
- Detection Distance: 2 cm to 20 cm
- Detection Angle: 35°
- Current Consumption: 6 mA at 5V; 10 mA at 3V
- Operating Temperature: -10°C to 50°C
- Dimensions: 41 x 17 x 11 mm
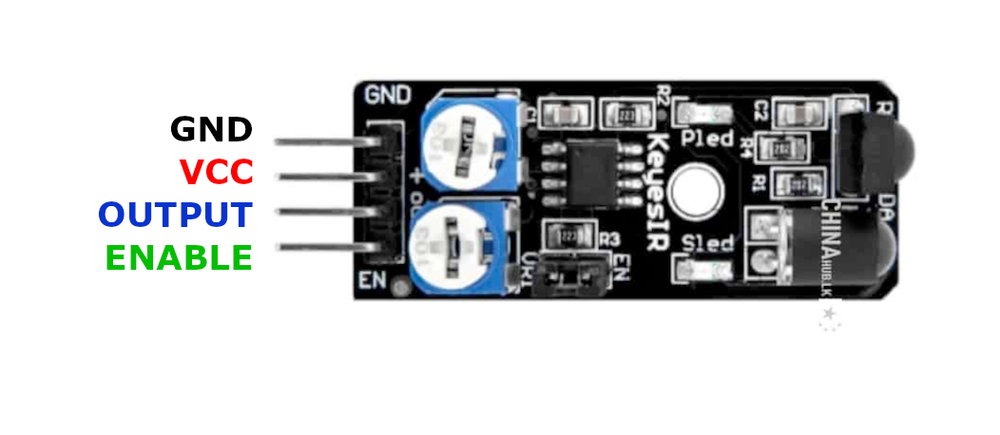
🔌 KY-032 Sensor Pinout
Below you can see the pinout for the KY-032 Infrared Obstacle Avoidance Sensor Module. The VCC pin is used to supply power to the sensor, and it typically requires 3.3V or 5V (refer to the datasheet for specific voltage requirements). The GND pin is the ground connection and must be connected to the ground of your ESP32!
GND:Connects to the ground of the circuit.VCC:Supplies power to the module, typically 3.3V or 5V.S (Signal):Outputs a digital signal indicating obstacle detection.EN (Enable):Can be used to enable or disable the sensor; by default, the sensor is always enabled.
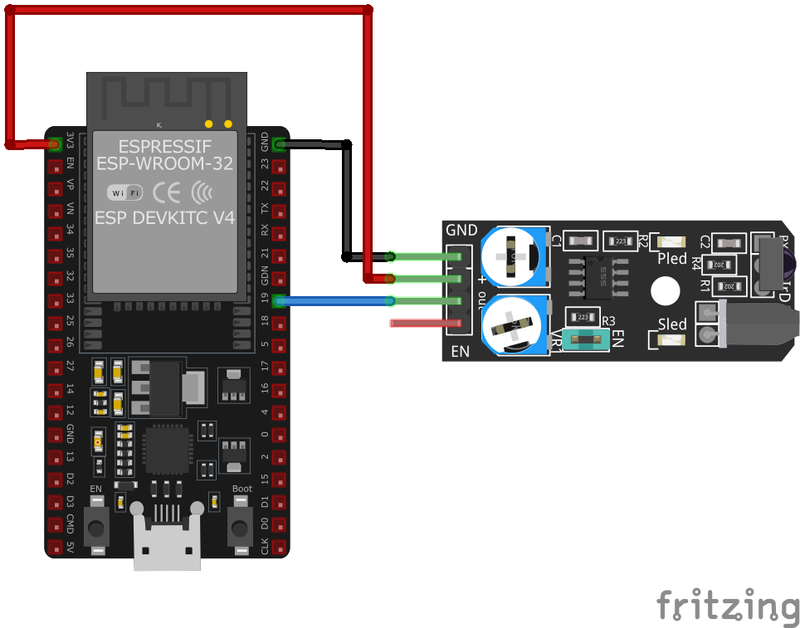
🧵 KY-032 Wiring with ESP32
Below you can see the wiring for the KY-032 Infrared Obstacle Avoidance Sensor Module with the ESP32. Connect the VCC pin of the sensor to the 3.3V pin on the ESP32 or external power supply for power and the GND pin of the sensor to the GND pin of the ESP32. Depending on the communication protocol of the sensor (e.g., I2C, SPI, UART, or analog), connect the appropriate data and clock or signal pins to compatible GPIO pins on the ESP32, as shown below in the wiring diagram.
GND:Connect to ESP32GND.VCC:Connect to ESP323.3Vor5V.S (Signal):Connect to a digital input pin on the ESP32 (e.g.,GPIO16).EN (Enable):If control over enabling is desired, connect to a GPIO pin; otherwise, leave it connected to VCC or use the default jumper setting.
🛠️ KY-032 Infrared Obstacle Avoidance Sensor Module Troubleshooting
This guide outlines a systematic approach to troubleshoot and resolve common problems with the . Start by confirming that the hardware connections are correct, as wiring mistakes are the most frequent cause of issues. If you are sure the connections are correct, follow the below steps to debug common issues.
❌ No Obstacle Detection
Issue: The sensor does not detect obstacles.
Solutions:
- Ensure proper wiring connections and verify the power supply voltage.
- Adjust the sensitivity and detection distance using the onboard potentiometers.
- Check for any obstructions or dirt on the sensor's infrared emitter and receiver.
⚠️ False Positives
Issue: The sensor indicates obstacles when none are present.
Solutions:
- Reduce the sensitivity using the potentiometer to prevent detection of distant or small objects.
- Ensure the sensor is not exposed to direct sunlight or strong ambient infrared sources.
- Verify that the sensor is securely mounted to prevent vibrations or movements that could cause false readings.
💻 Code Examples
Below you can find code examples of KY-032 Infrared Obstacle Avoidance Sensor Module with ESP32 in several frameworks:
If you encounter issues while using the KY-032 Infrared Obstacle Avoidance Sensor Module, check the Common Issues Troubleshooting Guide.

ESP32 KY-032 Arduino IDE Code Example
Fill in your main Arduino IDE sketch file with the following code to use the KY-032 Infrared Obstacle Avoidance Sensor Module:
int sensorPin = 10; // Sensor input pin
void setup() {
pinMode(sensorPin, INPUT);
Serial.begin(9600);
Serial.println("KY-032 Obstacle Detection Test");
}
void loop() {
int sensorValue = digitalRead(sensorPin);
if (sensorValue == LOW) { // Obstacle detected
Serial.println("Obstacle detected");
} else {
Serial.println("No obstacle");
}
delay(500);
}This Arduino code initializes the sensor input pin and serial communication. In the loop, it reads the sensor value and prints "Obstacle detected" or "No obstacle" to the serial monitor based on the sensor's digital output.
Connect your ESP32 to your computer via a USB cable, Ensure the correct Board and Port are selected under Tools, Click the "Upload" button in the Arduino IDE to compile and upload the code to your ESP32.

ESP32 KY-032 ESP-IDF Code ExampleExample in Espressif IoT Framework (ESP-IDF)
If you're using ESP-IDF to work with the KY-032 Infrared Obstacle Avoidance Sensor Module, here's how you can set it up and read data from the sensor. Fill in this code in the main ESP-IDF file:
#include <stdio.h>
#include "freertos/FreeRTOS.h"
#include "freertos/task.h"
#include "driver/gpio.h"
#define SENSOR_PIN GPIO_NUM_16
void app_main(void) {
gpio_config_t io_conf = {
.intr_type = GPIO_INTR_DISABLE,
.mode = GPIO_MODE_INPUT,
.pin_bit_mask = (1ULL << SENSOR_PIN),
.pull_up_en = GPIO_PULLUP_ENABLE
};
gpio_config(&io_conf);
printf("KY-032 Obstacle Detection Test\n");
while (1) {
int sensor_value = gpio_get_level(SENSOR_PIN);
if (sensor_value == 0) { // Obstacle detected
printf("Obstacle detected\n");
} else {
printf("No obstacle\n");
}
vTaskDelay(pdMS_TO_TICKS(500));
}
}This ESP-IDF code configures GPIO16 as an input with a pull-up resistor. It continuously reads the sensor's state and prints "Obstacle detected" or "No obstacle" to the console based on the sensor's output.
Update the I2C pins (I2C_MASTER_SDA_IO and I2C_MASTER_SCL_IO) to match your ESP32 hardware setup, Use idf.py build to compile the project, Use idf.py flash to upload the code to your ESP32.

ESP32 KY-032 ESPHome Code Example
Fill in this configuration in your ESPHome YAML configuration file (example.yml) to integrate the KY-032 Infrared Obstacle Avoidance Sensor Module
binary_sensor:
- platform: gpio
pin:
number: GPIO16
mode: INPUT_PULLUP
name: "KY-032 Obstacle Sensor"
device_class: motion
filters:
- invert:
on_press:
then:
- logger.log: "Obstacle detected"
on_release:
then:
- logger.log: "No obstacle detected"This ESPHome configuration sets up the KY-032 obstacle avoidance sensor as a binary sensor on GPIO16. It logs messages when an obstacle is detected and when it is cleared. The input is inverted to match the sensor's logic.
Upload this code to your ESP32 using the ESPHome dashboard or the esphome run command.

ESP32 KY-032 PlatformIO Code Example
For PlatformIO, make sure to configure the platformio.ini file with the appropriate environment and libraries, and then proceed with the code.
Configure platformio.ini
First, your platformio.ini should look like below. You might need to include some libraries as shown. Make sure to change the board to your ESP32:
[env:esp32]
platform = espressif32
board = esp32dev
framework = arduinoESP32 KY-032 PlatformIO Example Code
Write this code in your PlatformIO project under the src/main.cpp file to use the KY-032 Infrared Obstacle Avoidance Sensor Module:
#include <Arduino.h>
#define SENSOR_PIN 16
void setup() {
pinMode(SENSOR_PIN, INPUT_PULLUP);
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println("KY-032 Obstacle Sensor Test");
}
void loop() {
int sensor_value = digitalRead(SENSOR_PIN);
if (sensor_value == LOW) {
Serial.println("Obstacle detected");
} else {
Serial.println("No obstacle");
}
delay(500);
}This PlatformIO code sets up GPIO16 as an input with a pull-up resistor for the KY-032 sensor. It prints "Obstacle detected" or "No obstacle" to the serial monitor based on the sensor's state.
Upload the code to your ESP32 using the PlatformIO "Upload" button in your IDE or the pio run --target upload command.

ESP32 KY-032 MicroPython Code Example
Fill in this script in your MicroPython main.py file (main.py) to integrate the KY-032 Infrared Obstacle Avoidance Sensor Module with your ESP32.
import machine
import time
SENSOR_PIN = machine.Pin(16, machine.Pin.IN, machine.Pin.PULL_UP)
while True:
if SENSOR_PIN.value() == 0:
print("Obstacle detected")
else:
print("No obstacle")
time.sleep(0.5)This MicroPython script configures GPIO16 as an input with a pull-up resistor for the KY-032 sensor. It continuously checks for obstacles and prints the corresponding message every 500ms.
Upload this code to your ESP32 using a MicroPython-compatible IDE, such as Thonny, uPyCraft, or tools like ampy.
Conclusion
We went through technical specifications of KY-032 Infrared Obstacle Avoidance Sensor Module, its pinout, connection with ESP32 and KY-032 Infrared Obstacle Avoidance Sensor Module code examples with Arduino IDE, ESP-IDF, ESPHome and PlatformIO.