ESP32 MG90S Mini Servo
The MG90S is a robust micro servo motor designed for robotics and DIY projects. Operating on 4.8V to 6V, it provides up to 2.2 kg·cm torque, with a 0° to 180° range controlled via PWM signals. Weighing 13.4g, its durable metal gears and dimensions (22.8mm x 12.2mm x 31mm) make it ideal for applications requiring more torque and reliability.
🔗 Quick Links
🛒 MG90S Price
ℹ️ About MG90S Mini Servo
The MG90S is a metal-gear micro servo motor widely used in robotics, RC models, and DIY electronics. With its higher torque and durability, it outperforms plastic-gear alternatives like the SG90.
⚡ Key Features #
- Operating Voltage: 4.8V - 6V
- Torque: Up to 2.2 kg·cm at 4.8V
- Angular Range: 0° to 180° (PWM controlled)
- Pulse Width: 1ms (0°), 1.5ms (90°), 2ms (180°)
- Weight: ~13.4g
- Size: 22.8mm x 12.2mm x 31mm
- Metal Gears: Provides better strength and longevity compared to nylon-geared servos.
Looking for servo motor options for your ESP32-based projects? Check out this guide on top servo motors for ESP32.
⚙️ MG90S Sensor Technical Specifications
Below you can see the MG90S Mini Servo Technical Specifications. The sensor is compatible with the ESP32, operating within a voltage range suitable for microcontrollers. For precise details about its features, specifications, and usage, refer to the sensor’s datasheet.
- Type: servo
- Protocol: PWM
- Interface: PWM
- Torque: 2.2 kg·cm at 4.8V
- Operating Speed: 0.1 s/60° at 4.8V
- Operating Range: 0° to 180°
- Voltage: 4.8V to 6.0V
- Weight: 13.4 grams
- Gear Material: Metal
- Dimensions: 22.8mm x 12.2mm x 31mm
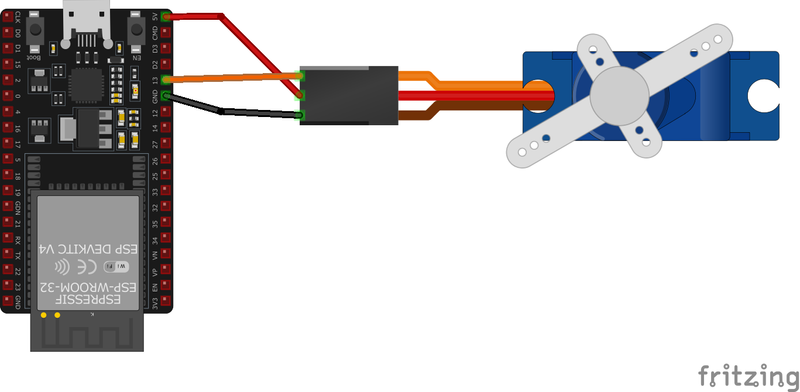
🔌 MG90S Sensor Pinout
Below you can see the pinout for the MG90S Mini Servo. The VCC pin is used to supply power to the sensor, and it typically requires 3.3V or 5V (refer to the datasheet for specific voltage requirements). The GND pin is the ground connection and must be connected to the ground of your ESP32!
- The servo's
GNDwire (brown) is used to complete the electrical circuit and must be connected to the ground of the ESP32 and/or the external power source. - The servo's
+5Vwire (red) supplies power to the servo motor and must receive 5 volts from the ESP32 or an external power source. - The servo's
DATAwire (orange) carries the PWM signal to control the servo's position and should be connected to a PWM-capable GPIO pin on the ESP32.
🧵 MG90S Wiring with ESP32
Below you can see the wiring for the MG90S Mini Servo with the ESP32. Connect the VCC pin of the sensor to the 3.3V pin on the ESP32 or external power supply for power and the GND pin of the sensor to the GND pin of the ESP32. Depending on the communication protocol of the sensor (e.g., I2C, SPI, UART, or analog), connect the appropriate data and clock or signal pins to compatible GPIO pins on the ESP32, as shown below in the wiring diagram.
- Connect the MG90S servo's signal wire (orange) to a PWM-capable GPIO pin on the ESP32 (e.g.,
GPIO 13). - Connect the power wire (red) to the
5Vpin on the ESP32 or an external power source. - Connect the ground wire (brown) to the ESP32's
GNDpin and ensure it's shared with the external power source if used.
🛠️ MG90S Mini Servo Troubleshooting
This guide outlines a systematic approach to troubleshoot and resolve common problems with the . Start by confirming that the hardware connections are correct, as wiring mistakes are the most frequent cause of issues. If you are sure the connections are correct, follow the below steps to debug common issues.
🔄 Servo Rotates Continuously Instead of Moving to Position
Issue: The MG90S servo rotates 360 degrees continuously rather than moving to a specified position.
Possible causes include using a continuous rotation version of the servo or incorrect pulse width modulation (PWM) signals.
Solution: Verify whether the servo is a standard positional model or a continuous rotation variant. Standard MG90S servos are designed for approximately 180-degree rotation. If the servo rotates continuously, it may be a continuous rotation model, which interprets PWM signals differently. Ensure that the PWM signals correspond to the servo's specifications, typically with pulse widths between 1ms and 2ms for standard servos.
⚠️ Limited Rotation Range
Issue: The MG90S servo does not achieve its full expected rotation range, moving less than 180 degrees.
Possible causes include incorrect PWM signal parameters or mechanical limitations.
Solution: Adjust the PWM signal to ensure it falls within the servo's required pulse width range. For the MG90S, pulse widths typically range from 0.8ms to 2.1ms to achieve the full rotation. Verify that there are no mechanical obstructions preventing movement.
⚡ Servo Jittering or Twitching
Issue: The MG90S servo exhibits jittery or twitchy movements during operation.
Possible causes include electrical noise, insufficient power supply, or signal interference.
Solution: Ensure a stable and adequate power supply to the servo, as voltage fluctuations can cause erratic behavior. Implement proper grounding and consider adding decoupling capacitors to filter out electrical noise. Check for any sources of signal interference and ensure that control signals are clean and within the appropriate voltage levels.
❌ Servo Not Responding to Control Signals
Issue: The MG90S servo does not respond to input control signals, remaining stationary.
Possible causes include incorrect wiring, faulty connections, or incompatible signal voltage levels.
Solution: Double-check all wiring connections to ensure they are correct and secure. Verify that the control signal wire is connected to a PWM-capable pin on the microcontroller. Ensure that the signal voltage levels are compatible with the servo's requirements, typically 3.3V or 5V depending on the microcontroller and servo specifications.
💻 Code Examples
Below you can find code examples of MG90S Mini Servo with ESP32 in several frameworks:
If you encounter issues while using the MG90S Mini Servo, check the Common Issues Troubleshooting Guide.

ESP32 MG90S Arduino IDE Code Example
You can find the ESP32 MG90S Arduino IDE code in General Servo sensor page.

ESP32 MG90S ESP-IDF Code ExampleExample in Espressif IoT Framework (ESP-IDF)
You can find the ESP32 MG90S ESP-IDF code in General Servo sensor page.

ESP32 MG90S ESPHome Code Example
You can find the ESP32 MG90S ESPHome code in General Servo sensor page.

ESP32 MG90S PlatformIO Code Example
You can find the ESP32 MG90S PlatformIO code in General Servo sensor page.

ESP32 MG90S MicroPython Code Example
You can find the ESP32 MG90S MicroPython code in General Servo sensor page.
Conclusion
We went through technical specifications of MG90S Mini Servo, its pinout, connection with ESP32 and MG90S Mini Servo code examples with Arduino IDE, ESP-IDF, ESPHome and PlatformIO.