ESP32 SG90 Mini Servo
The SG90 is a compact micro servo motor ideal for robotics and DIY projects. Operating on 4.8V to 6V, it delivers 1.8 kg·cm torque, with a 0° to 180° range controlled via PWM signals. Weighing 9g, its nylon gears and dimensions (22.8mm x 12.2mm x 28.5mm) make it perfect for lightweight, precise applications.
🔗 Quick Links
🛒 SG90 Price
ℹ️ About SG90 Mini Servo
The SG90 is a popular micro servo motor widely used in robotics, RC models, and DIY electronics. It offers precise angular control via PWM signals, making it ideal for small-scale projects that require lightweight and reliable actuation.
⚡ Key Features #
- Torque – 1.8 kg·cm at 4.8V, suitable for light-duty tasks.
- Operating Voltage – 4.8V to 6V, making it compatible with ESP32 and other microcontrollers.
- Angular Range – 0° to 180°, controlled via PWM signals.
- Compact & Lightweight – Weighs 9g with dimensions 22.8mm × 12.2mm × 28.5mm.
- Nylon Gears – Ensures smooth operation and durability for lightweight applications.
Looking for an ESP32-compatible servo motor project? Check out our ESP32 Servo Motor Guide!
⚙️ SG90 Sensor Technical Specifications
Below you can see the SG90 Mini Servo Technical Specifications. The sensor is compatible with the ESP32, operating within a voltage range suitable for microcontrollers. For precise details about its features, specifications, and usage, refer to the sensor’s datasheet.
- Type: servo
- Protocol: PWM
- Operating Voltage: 4.8V to 6V
- Torque: 1.8 kg·cm at 4.8V
- Operating Angle: 0° to 180°
- Pulse Width Control: 1ms (0°) to 2ms (180°)
- Dimensions: 22.8mm x 12.2mm x 28.5mm
- Weight: 9 grams
- Gear Material: Nylon
- Control Signal: PWM (50Hz)
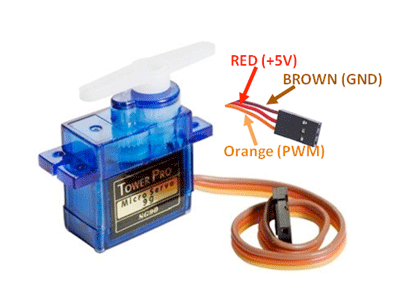
🔌 SG90 Sensor Pinout
Below you can see the pinout for the SG90 Mini Servo. The VCC pin is used to supply power to the sensor, and it typically requires 3.3V or 5V (refer to the datasheet for specific voltage requirements). The GND pin is the ground connection and must be connected to the ground of your ESP32!
- The servo's
GNDwire (brown) is used to complete the electrical circuit and must be connected to the ground of the ESP32 and/or the external power source. - The servo's
+5Vwire (red) supplies power to the servo motor and must receive 5 volts from the ESP32 or an external power source. - The servo's
DATAwire (orange) carries the PWM signal to control the servo's position and should be connected to a PWM-capable GPIO pin on the ESP32.
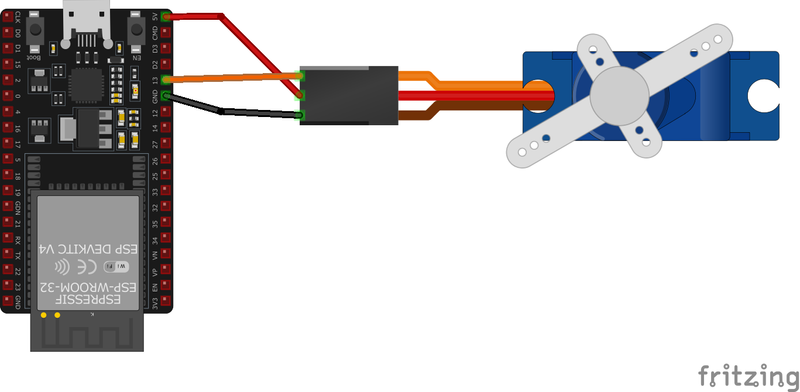
🧵 SG90 Wiring with ESP32
Below you can see the wiring for the SG90 Mini Servo with the ESP32. Connect the VCC pin of the sensor to the 3.3V pin on the ESP32 or external power supply for power and the GND pin of the sensor to the GND pin of the ESP32. Depending on the communication protocol of the sensor (e.g., I2C, SPI, UART, or analog), connect the appropriate data and clock or signal pins to compatible GPIO pins on the ESP32, as shown below in the wiring diagram.
- Connect the servo's signal wire (orange) to a PWM-capable GPIO pin on the ESP32 (e.g.,
GPIO 13). - Connect the power wire (red) to the
5Vpin on the ESP32 or an external power source. - Connect the ground wire (brown) to the ESP32's
GNDpin and ensure it's shared with the external power source if used.
🛠️ SG90 Mini Servo Troubleshooting
This guide outlines a systematic approach to troubleshoot and resolve common problems with the . Start by confirming that the hardware connections are correct, as wiring mistakes are the most frequent cause of issues. If you are sure the connections are correct, follow the below steps to debug common issues.
❌ Servo Not Responding or Moving Erratically
Issue: The SG90 servo does not move as expected or exhibits erratic behavior.
Possible causes include insufficient power supply, incorrect wiring, or improper PWM signal configuration.
Solution: Ensure the servo is powered by an adequate external power source, as the Arduino's 5V pin may not supply sufficient current. Verify that the control signal is connected to the correct PWM-capable pin on the microcontroller. Confirm that the PWM signal parameters match the servo's specifications, typically a 50Hz frequency with pulse widths between 1ms and 2ms corresponding to 0° to 180° positions.
🔄 Continuous Rotation Instead of Positional Movement
Issue: The SG90 servo rotates continuously instead of moving to a specified position.
Possible causes include the use of a continuous rotation servo variant or incorrect pulse width parameters.
Solution: Determine whether the servo is a standard positional servo or a continuous rotation model. For standard servos, ensure that the control pulses correspond to the correct positional commands. If using the Servo.attach() function in Arduino, specify appropriate minimum and maximum pulse widths to match the servo's requirements.
⚡ Servo Jittering or Twitching
Issue: The SG90 servo jitters or twitches when holding a position.
Possible causes include electrical noise, unstable power supply, or interference from other components.
Solution: Use a stable and adequately rated external power supply for the servo. Implement proper grounding and consider adding decoupling capacitors to filter out electrical noise. Ensure that the control signal is clean and free from interference, and avoid running servo wires parallel to high-power lines to minimize electromagnetic interference.
🔥 Servo Overheating
Issue: The SG90 servo becomes excessively hot during operation.
Possible causes include overloading the servo, continuous operation under high torque, or mechanical binding.
Solution: Check for any mechanical obstructions or excessive loads that may cause the servo to work harder than intended. Ensure that the servo is operating within its specified torque range and duty cycle. If the application requires continuous rotation under load, consider using a servo designed for such purposes or a geared motor with appropriate specifications.
💻 Code Examples
Below you can find code examples of SG90 Mini Servo with ESP32 in several frameworks:
If you encounter issues while using the SG90 Mini Servo, check the Common Issues Troubleshooting Guide.

ESP32 SG90 Arduino IDE Code Example
You can find the ESP32 SG90 Arduino IDE code in General Servo sensor page.

ESP32 SG90 ESP-IDF Code ExampleExample in Espressif IoT Framework (ESP-IDF)
You can find the ESP32 SG90 ESP-IDF code in General Servo sensor page.

ESP32 SG90 ESPHome Code Example
You can find the ESP32 SG90 ESPHome code in General Servo sensor page.

ESP32 SG90 PlatformIO Code Example
You can find the ESP32 SG90 PlatformIO code in General Servo sensor page.

ESP32 SG90 MicroPython Code Example
You can find the ESP32 SG90 MicroPython code in General Servo sensor page.
Conclusion
We went through technical specifications of SG90 Mini Servo, its pinout, connection with ESP32 and SG90 Mini Servo code examples with Arduino IDE, ESP-IDF, ESPHome and PlatformIO.