BMP388 / CJMCU-388 Barometric Pressure Sensor

View on Amazon
Overview
About BMP388 / CJMCU-388 Barometric Pressure Sensor
The BMP388, developed by Bosch Sensortec, is a next-generation barometric pressure and temperature sensor with higher accuracy, lower noise, and improved temperature stability. It outperforms its predecessors, including the BMP180 and BMP280, making it ideal for weather monitoring, altimetry, and drone altitude control.
⚡ Key Features
- Superior Accuracy & Low Noise – More precise and stable than BMP180 and BMP280.
- Wide Pressure Range – Ideal for altitude tracking, drones, and GPS applications.
- Integrated Temperature Sensor – Enhances environmental monitoring and altitude calculations.
- I²C & SPI Communication – Flexible connectivity with ESP32, Arduino, and other microcontrollers.
With its high precision and stability, the BMP388 is a top choice for advanced altitude and weather-based applications. 🚀
BMP388 Specifications
Complete technical specification details for BMP388 / CJMCU-388 Barometric Pressure Sensor
📊 Technical Parameters
BMP388 Pinout
The **BMP388** supports both **I²C** and **SPI** with enhanced precision:
Visual Pinout Diagram
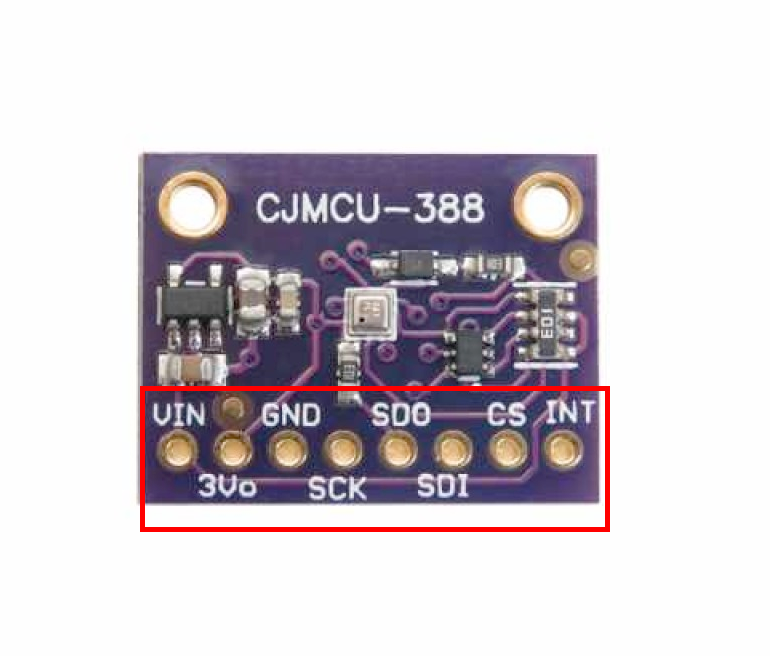

Pin Types
Quick Tips
**Dual Protocol**: Supports both I²C and SPI,📡 **I²C Address**: 0x76 or 0x77 (SDO pin selects),🌡️ **Temperature**: -40°C to +85°C, ±0.5°C accuracy
**Pressure**: 300-1250 hPa, ±0.5 hPa accuracy,📏 **Altitude**: ±0.25m precision (excellent for drones),⚡ **Power**: 3.3V ONLY (not 5V tolerant)
**High Precision**: Best in BMP series,🔇 **Low Noise**: Improved temperature stability,🎯 **Applications**: Drones, UAVs, precision altimeters, weather stations
Pin Descriptions
| Pin Name | Type | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
1 VCC | Power | Power input | 3.3V (not 5V tolerant) |
2 GND | Power | Ground connection | |
3 SDA | Communication | I²C data line | Connect to ESP32 GPIO21 |
4 SCL | Communication | I²C clock line | Connect to ESP32 GPIO22 |
5 CS | Communication | Chip select for SPI | Connect to GND for I²C mode |
6 SDO | Communication | SPI data out / I²C address | GND=0x76, VCC=0x77 for I²C |
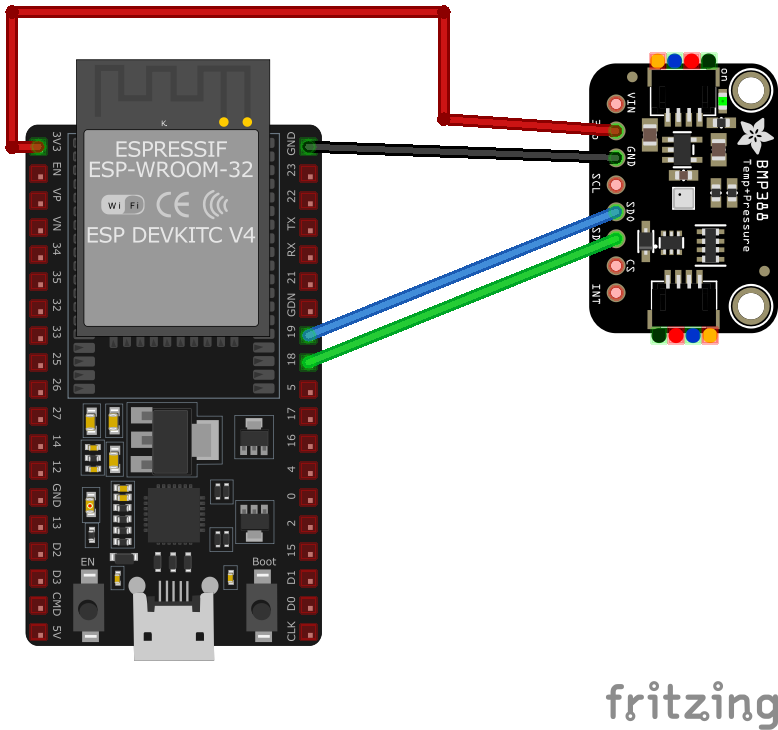
Wiring BMP388 to ESP32
To interface the **BMP388** with an **ESP32** using **I²C**:
Visual Wiring Diagram
Connection Status
Protocol
Pin Connections
| BMP388 Pin | Connection | ESP32 Pin | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
1 VCC Required | 3.3V | Power supply (3.3V only) | |
2 GND Required | GND | Ground | |
3 SDA Required | GPIO21 | I²C data line | |
4 SCL Required | GPIO22 | I²C clock line | |
5 CS Required | GND | Set to GND for I²C mode |
**I²C Address**: 0x76 (SDO→GND) or 0x77 (SDO→VCC)
**Power**: 3.3V ONLY - do NOT use 5V
**High Precision**: Best accuracy in BMP series
**CSB Pin**: Must connect to GND for I²C mode
**Drones**: Ideal for UAV altitude control
**Fast**: Quick conversion times
BMP388 Troubleshooting
Common issues and solutions to help you get your sensor working
Common Issues
Issue: The Arduino IDE cannot find the required BMP388 library.
Solution: Ensure that you have installed the Adafruit BMP3XX library from the Arduino Library Manager. Restart the Arduino IDE after installation.
Issue: The BMP388 sensor fails to initialize, and the error message Could not find a valid BMP388 sensor appears.
Solution: Check the wiring connections and ensure the sensor receives 3.3V power. Use an I²C scanner to detect the sensor's address.
Issue: The sensor outputs incorrect pressure values, leading to inaccurate altitude measurements.
Solution: Verify that the reference sea-level pressure value is set correctly and recalibrate the sensor if needed.
Debugging Tips
Use the Serial Monitor to check for error messages and verify the sensor's output. Add debug prints in your code to track the sensor's state.
Use a multimeter to verify voltage levels and check for continuity in your connections. Ensure the power supply is stable and within the sensor's requirements.
Additional Resources
BMP388 Programming Examples
Ready-to-use code examples for different platforms and frameworks
#include <Wire.h>
#include <Adafruit_Sensor.h>
#include <Adafruit_BMP3XX.h>
Adafruit_BMP3XX bmp;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
if (!bmp.begin(0x76)) {
Serial.println("Could not find a valid BMP388 sensor, check wiring!");
while (1);
}
}
void loop() {
Serial.print("Temperature: ");
Serial.print(bmp.temperature);
Serial.println(" *C");
Serial.print("Pressure: ");
Serial.print(bmp.pressure / 100.0);
Serial.println(" hPa");
delay(2000);
}This Arduino code initializes the BMP388 sensor using the Adafruit BMP3XX library. It reads temperature and pressure values and prints them to the Serial Monitor every two seconds.
#include "bmp388.h"
#include "esp_log.h"
#define I2C_MASTER_SCL_IO 22
#define I2C_MASTER_SDA_IO 21
#define I2C_MASTER_FREQ_HZ 100000
#define BMP388_ADDR 0x76
static const char *TAG = "BMP388";
void app_main() {
ESP_LOGI(TAG, "Initializing BMP388...");
bmp388_dev dev;
bmp388_init(&dev, I2C_MASTER_SCL_IO, I2C_MASTER_SDA_IO, I2C_MASTER_FREQ_HZ, BMP388_ADDR);
while (1) {
bmp388_data data;
bmp388_read(&dev, &data);
ESP_LOGI(TAG, "Temperature: %.2f°C", data.temperature);
ESP_LOGI(TAG, "Pressure: %.2f hPa", data.pressure);
vTaskDelay(2000 / portTICK_PERIOD_MS);
}
}This ESP-IDF code configures the ESP32 to interface with the BMP388 sensor over I²C. The bmp388_init function initializes the sensor, and bmp388_read fetches pressure and temperature readings.
sensor:
- platform: bmp388
temperature:
name: "BMP388 Temperature"
pressure:
name: "BMP388 Pressure"
address: 0x76This ESPHome configuration enables the BMP388 sensor to provide temperature and pressure readings over I²C, using the default address 0x76.
platformio.ini
[env:esp32dev]
platform = espressif32
board = esp32dev
framework = arduino
lib_deps =
adafruit/Adafruit BMP3XX Library
wire
monitor_speed = 115200main.cpp
#include <Wire.h>
#include <Adafruit_BMP3XX.h>
Adafruit_BMP3XX bmp;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
if (!bmp.begin(0x76)) {
Serial.println("Could not find a valid BMP388 sensor, check wiring!");
while (1);
}
}
void loop() {
Serial.print("Temperature: ");
Serial.print(bmp.temperature);
Serial.println(" *C");
Serial.print("Pressure: ");
Serial.print(bmp.pressure / 100.0);
Serial.println(" hPa");
delay(2000);
}This PlatformIO code integrates the BMP388 sensor to read temperature and pressure values, printing them every two seconds.
Wrapping Up BMP388
The ESP32 BMP388 / CJMCU-388 Barometric Pressure Sensor is a powerful environment sensor that offers excellent performance and reliability. With support for multiple development platforms including Arduino, ESP-IDF, ESPHome, PlatformIO, and MicroPython, it's a versatile choice for your IoT projects.
Best Practices
For optimal performance, ensure proper wiring and follow the recommended configuration for your chosen development platform.
Safety First
Always verify power supply requirements and pin connections before powering up your project to avoid potential damage.
Ready to Start Building?
Now that you have all the information you need, it's time to integrate the BMP388 into your ESP32 project and bring your ideas to life!
Explore Alternative Sensors
Looking for alternatives to the BMP388? Check out these similar sensors that might fit your project needs.
The DHT21 is a reliable sensor for measuring temperature and humidity, offering calibrated digital output and ease of integration with...
The AHT20 datasheet provides comprehensive technical details about the AHT20 digital temperature and humidity sensor, a highly accurate and...