ESP32 SHT21 / HTU21 / GY-21 / SI7021 Temperature and Humidity Sensor Pinout
Overview
The SHT21, HTU21, GY-21, and SI7021 sensors utilize I2C for reliable communication and provide calibrated, linearized temperature and humidity readings. Their compact form factor and low power consumption make them ideal for precise environmental monitoring.
About SHT21 / HTU21 / GY-21 / SI7021 Temperature and Humidity Sensor
The SHT21, HTU21, GY-21, and SI7021 are compact digital temperature and humidity sensors that provide high-precision measurements. Using the I²C communication protocol, they are ideal for HVAC systems, data loggers, weather stations, and consumer electronics.
⚡ Key Features
- High Accuracy & Stability – Reliable temperature and humidity sensing.
- I²C Communication – Easy integration with ESP32, Arduino, and other microcontrollers.
- Compact & Energy-Efficient – Ideal for low-power and battery-powered applications.
- Versatile Applications – Used in climate control, weather monitoring, and industrial automation.
🔗 Looking for alternatives in the SHT series? Check out:
Where to Buy SHT21 / HTU21 / GY-21 / SI7021 Temperature and Humidity Sensor



Prices are subject to change. We earn from qualifying purchases as an Amazon Associate.
SHT21 / HTU21 / GY-21 / SI7021 Datasheet and Technical Specifications
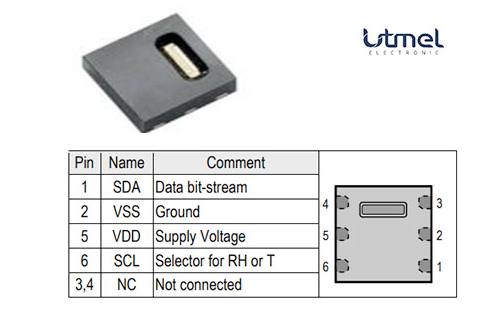
SHT21 / HTU21 / GY-21 / SI7021 Pinout Diagram
The VCC pin is used to supply power to the sensor, and it typically requires 3.3V or 5V (refer to the datasheet for specific voltage requirements). The GND pin is the ground connection and must be connected to the ground of your ESP32.
The Pinout for these sensors is as follows:
- VCC: Power supply voltage (2.1V to 3.6V).
- GND: Ground.
- SDA: Serial Data Line for I2C communication.
- SCL: Serial Clock Line for I2C communication.
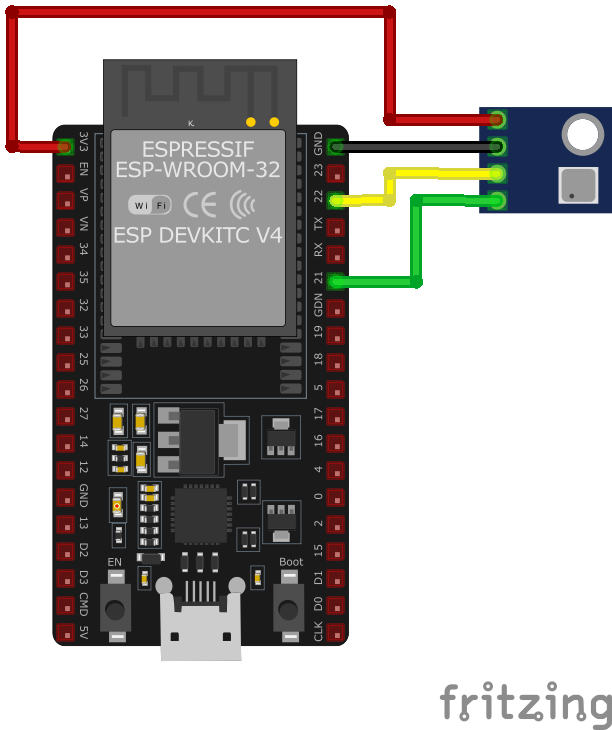
SHT21 / HTU21 / GY-21 / SI7021 Wiring with ESP32
- Connect VCC to the 3.3V pin on the ESP32.
- Connect GND to the ground (GND) of the ESP32.
- Connect SDA to the ESP32's GPIO21 (default I2C data pin).
- Connect SCL to the ESP32's GPIO22 (default I2C clock pin).
- Place pull-up resistors (10kΩ) between SDA and VCC, and SCL and VCC, to ensure reliable communication.
SHT21 / HTU21 / GY-21 / SI7021 Troubleshooting Guide
Common Issues
💻 Compilation Errors with SHT21 Library
Issue: When compiling code that interfaces with the SHT21 sensor using the LibHumidity library, errors such as 'class TwoWire' has no member named 'send' and 'class TwoWire' has no member named 'receive' are encountered.
Possible causes include the use of outdated functions in the library that are incompatible with the current Wire library, which now uses write() and read() methods instead of send() and receive().
Solution: Update the LibHumidity library by replacing instances of send() with write() and receive() with read(). Alternatively, consider using a more recent library that supports the SHT21 sensor and is compatible with the current Wire library implementation.
🔒 Permission Denied Error on Raspberry Pi
Issue: When running a Python script to read data from the SHT21 sensor on a Raspberry Pi, the error [Errno 13] Permission denied: '/dev/i2c-1' is encountered.
Possible causes include insufficient permissions to access the I2C bus device file.
Solution: Execute the Python script with elevated privileges by prefixing the command with sudo. For example, run sudo python sht21.py to grant the necessary permissions to access the I2C bus.
⚠️ Incorrect Temperature and Humidity Readings
Issue: The SHT21 sensor returns incorrect temperature and humidity values, such as 988 instead of the expected readings.
Possible causes include improper wiring, incorrect I2C address configuration, or sensor initialization issues.
Solution: Verify that the sensor is correctly wired to the microcontroller, ensuring proper connections for power, ground, and I2C data lines. Confirm that the correct I2C address (typically 0x40) is specified in your code. Ensure that the sensor is properly initialized in the software, and consider using a reliable library compatible with the SHT21 sensor.
🔌 Interfacing Issues with SHT21 Sensor
Issue: Difficulty in establishing I2C communication with the SHT21 sensor, leading to unsuccessful data retrieval.
Possible causes include incorrect I2C initialization, improper sensor configuration, or timing issues in the communication protocol.
Solution: Ensure that the I2C bus is correctly initialized with the appropriate settings, including clock speed and addressing. Review the sensor's datasheet to confirm proper configuration and command sequences. Implement necessary delays as specified in the sensor's communication protocol to accommodate timing requirements.
Debugging Tips
🔍 Serial Monitor
Use the Serial Monitor to check for error messages and verify the sensor's output. Add debug prints in your code to track the sensor's state.
⚡ Voltage Checks
Use a multimeter to verify voltage levels and check for continuity in your connections. Ensure the power supply is stable and within the sensor's requirements.
Additional Resources
SHT21 / HTU21 / GY-21 / SI7021 Code Examples
Arduino Example
#include <Wire.h>
#include "SHT21.h"
SHT21 sht;
void setup() {
Wire.begin();
Serial.begin(9600);
}
void loop() {
float temperature = sht.getTemperature();
float humidity = sht.getHumidity();
Serial.print("Temperature: ");
Serial.print(temperature);
Serial.println(" °C");
Serial.print("Humidity: ");
Serial.print(humidity);
Serial.println(" %");
delay(2000);
}ESP-IDF Example
#include <stdio.h>
#include "freertos/FreeRTOS.h"
#include "freertos/task.h"
#include "driver/i2c.h"
#define I2C_MASTER_SCL_IO 22 /!< GPIO number used for I2C master clock /
#define I2C_MASTER_SDA_IO 21 /!< GPIO number used for I2C master data /
#define I2C_MASTER_NUM I2C_NUM_0 /!< I2C master I2C port number /
#define I2C_MASTER_FREQ_HZ 100000 /!< I2C master clock frequency /
#define SHT21_SENSOR_ADDR 0x40 /!< I2C address /
void read_sensor() {
uint8_t data[3];
uint8_t cmd = 0xF5; // Humidity command
i2c_master_write_to_device(I2C_MASTER_NUM, SHT21_SENSOR_ADDR, &cmd, 1, pdMS_TO_TICKS(1000));
vTaskDelay(pdMS_TO_TICKS(50));
i2c_master_read_from_device(I2C_MASTER_NUM, SHT21_SENSOR_ADDR, data, 3, pdMS_TO_TICKS(1000));
uint16_t raw_humidity = (data[0] << 8) | (data[1] & 0xFC);
float humidity = -6.0 + 125.0 (raw_humidity / 65536.0);
cmd = 0xF3; // Temperature command
i2c_master_write_to_device(I2C_MASTER_NUM, SHT21_SENSOR_ADDR, &cmd, 1, pdMS_TO_TICKS(1000));
vTaskDelay(pdMS_TO_TICKS(50));
i2c_master_read_from_device(I2C_MASTER_NUM, SHT21_SENSOR_ADDR, data, 3, pdMS_TO_TICKS(1000));
uint16_t raw_temperature = (data[0] << 8) | (data[1] & 0xFC);
float temperature = -46.85 + 175.72 (raw_temperature / 65536.0);
printf("Temperature: %.2f °C\n", temperature);
printf("Humidity: %.2f %%\n", humidity);
}
void app_main() {
// Initialize I2C
i2c_config_t conf = {
.mode = I2C_MODE_MASTER,
.sda_io_num = I2C_MASTER_SDA_IO,
.scl_io_num = I2C_MASTER_SCL_IO,
.sda_pullup_en = GPIO_PULLUP_ENABLE,
.scl_pullup_en = GPIO_PULLUP_ENABLE,
.master.clk_speed = I2C_MASTER_FREQ_HZ,
};
i2c_param_config(I2C_MASTER_NUM, &conf);
i2c_driver_install(I2C_MASTER_NUM, conf.mode, 0, 0, 0);
while (1) {
read_sensor();
vTaskDelay(pdMS_TO_TICKS(2000));
}
}ESPHome Example
sensor:
- platform: sht3x
address: 0x40
temperature:
name: "Room Temperature"
humidity:
name: "Room Humidity"
update_interval: 60ssht3x platform for SHT21-compatible sensors. It defines two sensor entities for temperature and humidity, with human-readable names. The update_interval is set to 60 seconds, ensuring periodic updates of the readings.PlatformIO Example
platformio.ini
[env:esp32dev]
platform = espressif32
board = esp32dev
framework = arduino
lib_deps =
DFRobot/SHT21 @ ^1.0.0
monitor_speed = 115200PlatformIO Example Code
#include <Wire.h>
#include "SHT21.h"
SHT21 sht;
void setup() {
Wire.begin();
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println("SHT21 Sensor Example");
}
void loop() {
float temperature = sht.getTemperature();
float humidity = sht.getHumidity();
if (!isnan(temperature) && !isnan(humidity)) {
Serial.print("Temperature: ");
Serial.print(temperature);
Serial.println(" °C");
Serial.print("Humidity: ");
Serial.print(humidity);
Serial.println(" %");
} else {
Serial.println("Failed to read from sensor");
}
delay(2000);
}MicroPython Example
from machine import Pin, I2C
from time import sleep
SENSOR_ADDR = 0x40
CMD_TEMP = 0xF3
CMD_HUM = 0xF5
def read_sensor(i2c, cmd):
i2c.writeto(SENSOR_ADDR, bytearray([cmd]))
sleep(0.05)
data = i2c.readfrom(SENSOR_ADDR, 3)
return (data[0] << 8 | data[1]) & 0xFFFC
def calc_temperature(raw_temp):
return -46.85 + 175.72 (raw_temp / 65536.0)
def calc_humidity(raw_hum):
return -6.0 + 125.0 (raw_hum / 65536.0)
i2c = I2C(0, scl=Pin(22), sda=Pin(21))
while True:
raw_temp = read_sensor(i2c, CMD_TEMP)
raw_hum = read_sensor(i2c, CMD_HUM)
temperature = calc_temperature(raw_temp)
humidity = calc_humidity(raw_hum)
print("Temperature: {:.2f} °C".format(temperature))
print("Humidity: {:.2f} %".format(humidity))
sleep(2)Conclusion
The ESP32 SHT21 / HTU21 / GY-21 / SI7021 Temperature and Humidity Sensor is a powerful environment sensor that offers excellent performance and reliability. With support for multiple development platforms including Arduino, ESP-IDF, ESPHome, PlatformIO, and MicroPython, it's a versatile choice for your IoT projects.
For optimal performance, ensure proper wiring and follow the recommended configuration for your chosen development platform.
Always verify power supply requirements and pin connections before powering up your project to avoid potential damage.