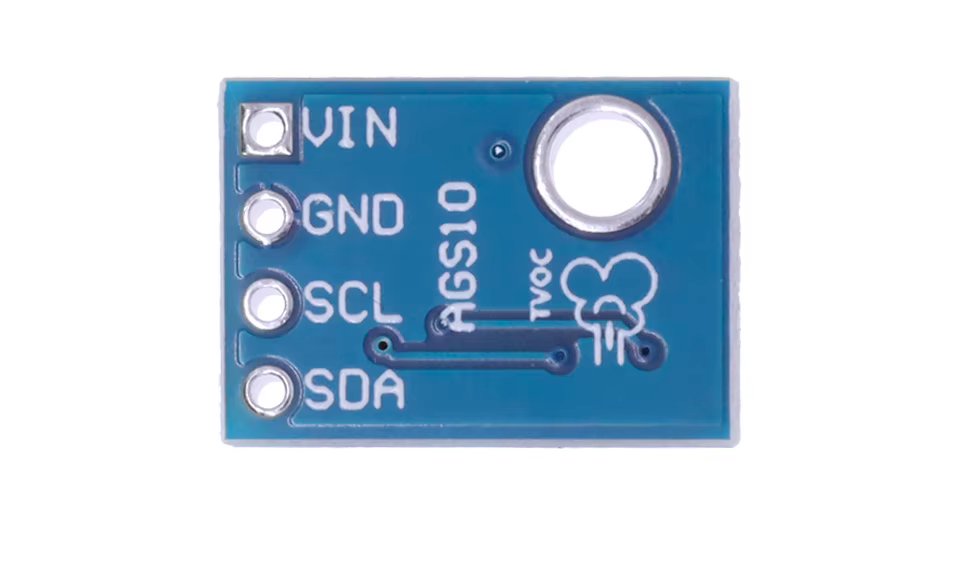
AGS10 Sensor

View on Amazon
Overview
About AGS10 Sensor
The AGS10 is a compact and highly sensitive gas sensor designed for air quality monitoring and gas detection applications. It can detect various gases, including volatile organic compounds (VOCs), making it useful for indoor air monitoring, industrial safety, and smart home projects.
⚡ Key Features
- High Sensitivity to VOCs – Ideal for air quality monitoring and gas detection.
- Compact & Low Power – Suitable for battery-powered applications.
- Fast Response & Recovery Time – Ensures real-time gas monitoring.
- I²C Communication – Simplifies integration with ESP32 and other microcontrollers.
Get Your AGS10



Prices are subject to change. We earn from qualifying purchases as an Amazon Associate.
AGS10 Specifications
Complete technical specification details for AGS10 Sensor
📊 Technical Parameters
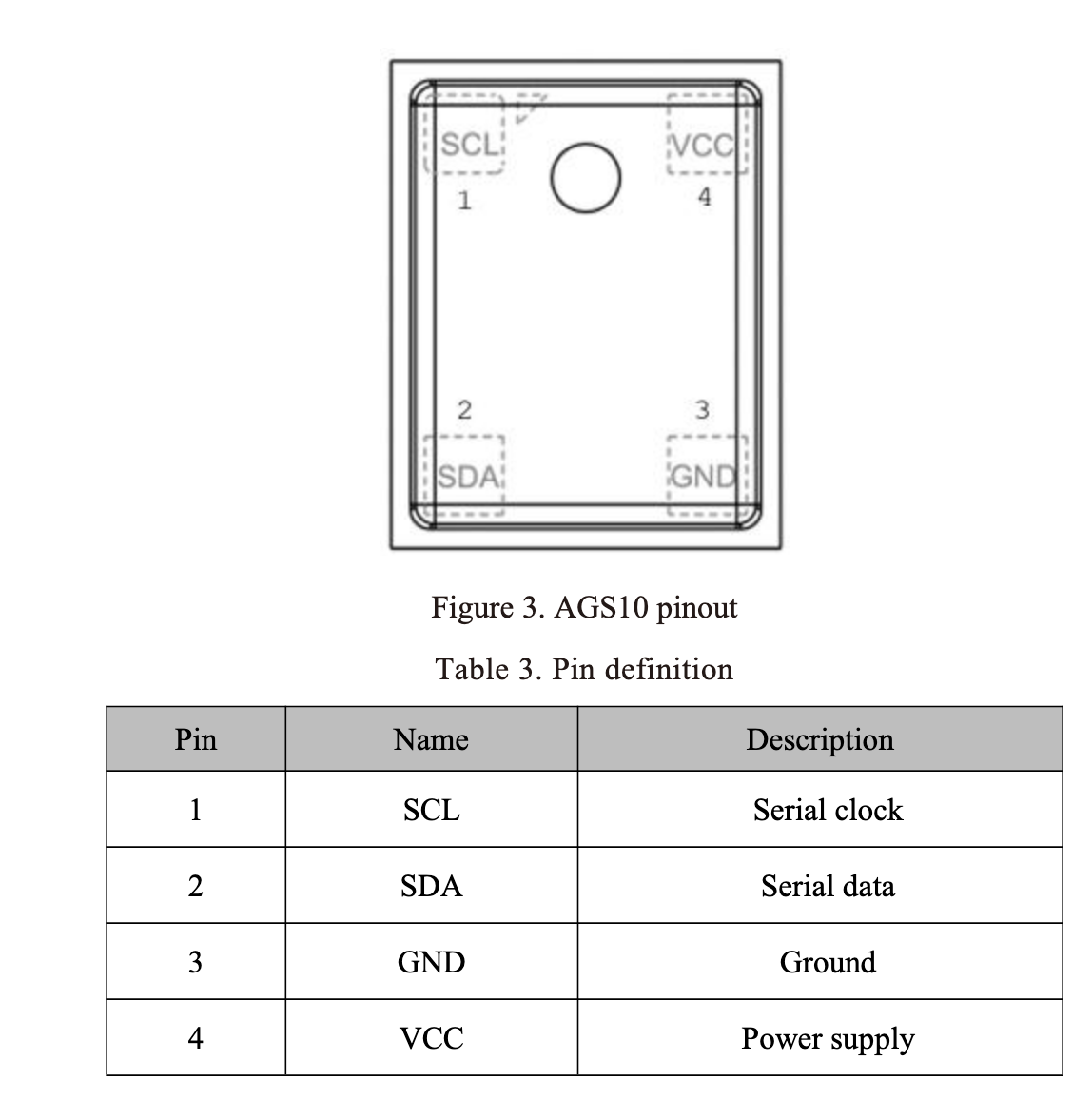
AGS10 Pinout
Visual Pinout Diagram

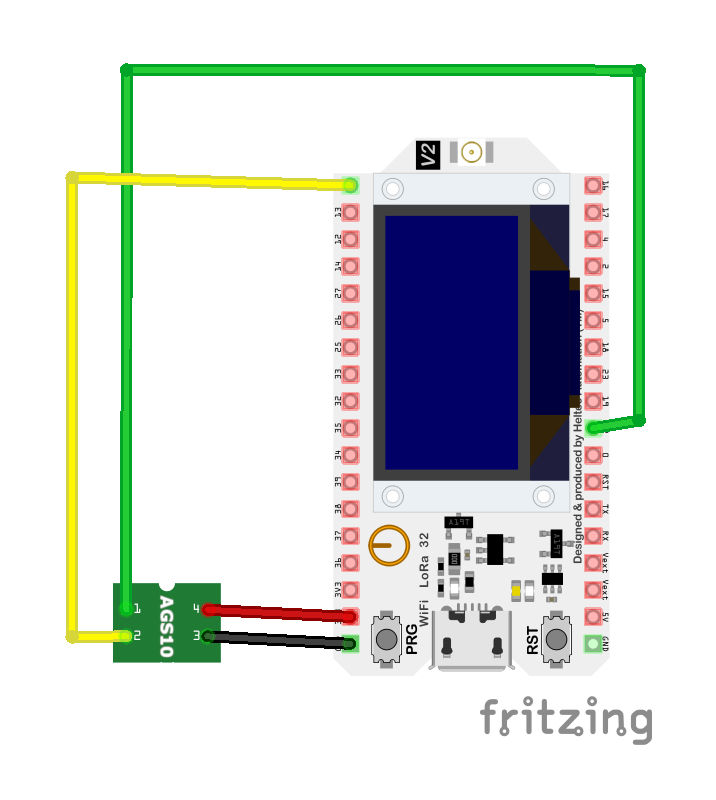
Wiring AGS10 to ESP32
Visual Wiring Diagram
Protocol
AGS10 Troubleshooting
Common issues and solutions to help you get your sensor working
Common Issues
Issue: When using the AGS10 sensor with an ESP32-S2 microcontroller, the following error is encountered: The crc check failed. This issue arises despite the sensor functioning correctly on standard ESP32 boards.
Possible causes include the AGS10 sensor's requirement for an I2C bus speed not exceeding 15kHz, which may not be properly configured on the ESP32-S2.
Solution: Ensure that the I2C bus frequency is explicitly set to 15kHz in your configuration. In ESPHome, this can be achieved by specifying frequency: 15kHz in the I2C setup. Additionally, verify that the ESP32-S2 supports the specified I2C frequency and that there are no hardware limitations affecting communication.
Issue: Integrating the AGS10 sensor with a TCA9548A I2C multiplexer in ESPHome results in configuration errors, such as: required key not provided.
Possible causes include incorrect or incomplete configuration settings in the ESPHome YAML file, particularly when defining the multiplexer channels.
Solution: Review the ESPHome configuration to ensure that all required keys and parameters are correctly specified. Each multiplexer channel should be properly defined with the necessary settings. Consulting the ESPHome documentation for guidance on configuring I2C multiplexers can provide clarity.
Issue: When compiling code that includes the AGS10 sensor library, errors such as: invalid conversion from 'uint8_t' {aka 'unsigned char'} to 'uint8_t*' {aka 'unsigned char*'} occur.
Possible causes include incompatibilities in the AGS10 library when used with certain microcontrollers, such as boards other than the Arduino Uno.
Solution: Consider using a modified version of the AGS10 library that addresses these compatibility issues. For instance, a fork of the library tailored for ESP32 is available and may resolve the compilation errors.
Issue: The AGS10 sensor requires an I2C bus speed not exceeding 15kHz. Failure to configure this can lead to communication errors or sensor malfunction.
Possible causes include the default I2C bus frequency being set higher than the sensor's specifications.
Solution: Explicitly set the I2C bus frequency to 15kHz in your microcontroller's configuration. In ESPHome, this can be done by adding frequency: 15kHz to the I2C configuration section.
Debugging Tips
Use the Serial Monitor to check for error messages and verify the sensor's output. Add debug prints in your code to track the sensor's state.
Use a multimeter to verify voltage levels and check for continuity in your connections. Ensure the power supply is stable and within the sensor's requirements.
Additional Resources
AGS10 Programming Examples
Ready-to-use code examples for different platforms and frameworks
#include <Wire.h>
#define I2C_ADDRESS 0xXX // Replace with the AGS10 I2C address
#define SDA_PIN 21 // I2C SDA pin for ESP32
#define SCL_PIN 22 // I2C SCL pin for ESP32
void setup() {
Wire.begin(SDA_PIN, SCL_PIN);
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println("AGS10 I2C Test");
}
void loop() {
Wire.beginTransmission(I2C_ADDRESS);
Wire.write(0x00); // Example register or command
Wire.endTransmission();
Wire.requestFrom(I2C_ADDRESS, 2);
if (Wire.available() == 2) {
int highByte = Wire.read();
int lowByte = Wire.read();
int sensorValue = (highByte << 8) | lowByte;
Serial.print("Sensor Value: ");
Serial.println(sensorValue);
}
delay(1000);
}#include <stdio.h>
#include "driver/i2c.h"
#define I2C_MASTER_SCL_IO 22 // GPIO for SCL
#define I2C_MASTER_SDA_IO 21 // GPIO for SDA
#define I2C_MASTER_NUM I2C_NUM_1
#define I2C_MASTER_FREQ_HZ 100000
void app_main() {
i2c_config_t conf;
conf.mode = I2C_MODE_MASTER;
conf.sda_io_num = I2C_MASTER_SDA_IO;
conf.scl_io_num = I2C_MASTER_SCL_IO;
conf.sda_pullup_en = GPIO_PULLUP_ENABLE;
conf.scl_pullup_en = GPIO_PULLUP_ENABLE;
conf.master.clk_speed = I2C_MASTER_FREQ_HZ;
i2c_param_config(I2C_MASTER_NUM, &conf);
i2c_driver_install(I2C_MASTER_NUM, conf.mode, 0, 0, 0);
// Add code to read from AGS10 via I2C
}i2c_param_config() and i2c_driver_install() functions set up the I2C master for communication. You can add commands to communicate with the AGS10 sensor by sending and receiving I2C data after the initialization.sensor:
- platform: ags10
tvoc:
name: TVOCplatformio.ini
[env:esp32]
platform = espressif32
board = esp32dev
framework = espidf
monitor_speed = 115200main.cpp
#include <Wire.h>
#define I2C_ADDRESS 0xXX // Replace with the AGS10 I2C address
#define SDA_PIN 21 // I2C SDA pin for ESP32
#define SCL_PIN 22 // I2C SCL pin for ESP32
void setup() {
Wire.begin(SDA_PIN, SCL_PIN);
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println("AGS10 I2C Test");
}
void loop() {
Wire.beginTransmission(I2C_ADDRESS);
Wire.write(0x00); // Example register or command
Wire.endTransmission();
Wire.requestFrom(I2C_ADDRESS, 2);
if (Wire.available() == 2) {
int highByte = Wire.read();
int lowByte = Wire.read();
int sensorValue = (highByte << 8) | lowByte;
Serial.print("Sensor Value: ");
Serial.println(sensorValue);
}
delay(1000);
}platformio.ini file.from machine import I2C, Pin
from time import sleep
# Initialize I2C
i2c = I2C(0, scl=Pin(22), sda=Pin(21))
address = 0xXX # Replace with the AGS10 I2C address
while True:
# Write command and read data
i2c.writeto(address, b'\x00') # Example register or command
data = i2c.readfrom(address, 2)
# Combine high and low bytes into a 16-bit value
sensor_value = (data[0] << 8) | data[1]
print(f"Sensor Value: {sensor_value}")
sleep(1)Wrapping Up AGS10
The ESP32 AGS10 Sensor is a powerful Air Quality sensor that offers excellent performance and reliability. With support for multiple development platforms including Arduino, ESP-IDF, ESPHome, PlatformIO, and MicroPython, it's a versatile choice for your IoT projects.
Best Practices
For optimal performance, ensure proper wiring and follow the recommended configuration for your chosen development platform.
Safety First
Always verify power supply requirements and pin connections before powering up your project to avoid potential damage.
Ready to Start Building?
Now that you have all the information you need, it's time to integrate the AGS10 into your ESP32 project and bring your ideas to life!
Explore Alternative Sensors
Looking for alternatives to the AGS10? Check out these similar sensors that might fit your project needs.
The MH-Z19 is a high-accuracy CO₂ sensor using NDIR technology, suitable for air quality monitoring. It supports UART and PWM communication,...
The MiCS-4514 is a dual gas sensor capable of detecting oxidizing gases (e.g., NO₂) and reducing gases (e.g., CO, NH₃). It provides analog...